传感器网络节点拓朴

(注:本文是译文,Original text from white paper of IEC)
Generally, a WSN consists of a number of sensor network nodes and a gateway for the connection to the internet. The general deployment process of a WSN is as follows (see Figure 3-8): firstly, the sensor network nodes broadcast their status to the surroundings and receive status from other nodes to detect each other. Secondly, the sensor network nodes are organized into a connected network according to a certain topology (linear, star, tree, mesh, etc.). Finally, suitable paths are computed on the constructed network for transmitting the sensing data.
通常,WSN由多个传感器网络节点和用于连接到因特网的网关组成。WSN的一般部署过程如下(见图3-8):FI,传感器网络节点将它们的状态广播到周围环境,并从其他节点接收状态以检测彼此。其次,将传感器网络节点按照一定的拓扑结构(线性、星形、树、网格等)组织成连接网络。最后,在所构建的网络上计算合适的路径来传输感测数据。
The power of sensor network nodes is usually provided by batteries, so the transmission distance of WSN nodes is short. The transmission distance can be up to 800 to 1 000 meters in the open outdoor environment with line of sight. It will sharply decline in the case of a sheltered indoor environment to an estimated few meters. In order to expand the coverage of a network, the sensor network uses multi-hop transmission mode. That is to say the sensor network nodes are both transmitter and receiver.
传感器网络节点的功率通常由电池提供,因此无线传感器网络节点的传输距离较短。在室外有视线的户外环境中,传输距离可达800至1米000。在急剧下降的情况下,室内环境估计数米。为了扩展网络的覆盖范围,传感器网络采用多跳传输模式。也就是说,传感器网络节点都是发射机和接收机。
The first sensor network node, the source node, sends data to a nearby node for data transmission to the gateway. The nearby node forwards the data to one of its nearby nodes that are on the path towards the gateway. The forwarding is repeated until the data arrives at the gateway, the destination. The protocols and some implementation techniques of WSNs can be adapted to the mature architecture and technologies of wireless and wired computer networks. However, the features of WSNs are self-organization, self-adaption, limited nodes energy, and unstable transmission links.
第一传感器网络节点,源节点,将数据发送到附近的节点,以便数据传输到网关。附近的节点将数据转发到位于网关的路径上的附近节点之一。转发是重复的,直到数据到达网关目的地。无线传感器网络的协议和一些实现技术可以适应无线和有线计算机网络的成熟结构和技术。然而,无线传感器网络的特点是自组织、自适应、节点能量有限、传输链路不稳定。
Self-organizing and reliable networking technology
自组织可靠网络技术
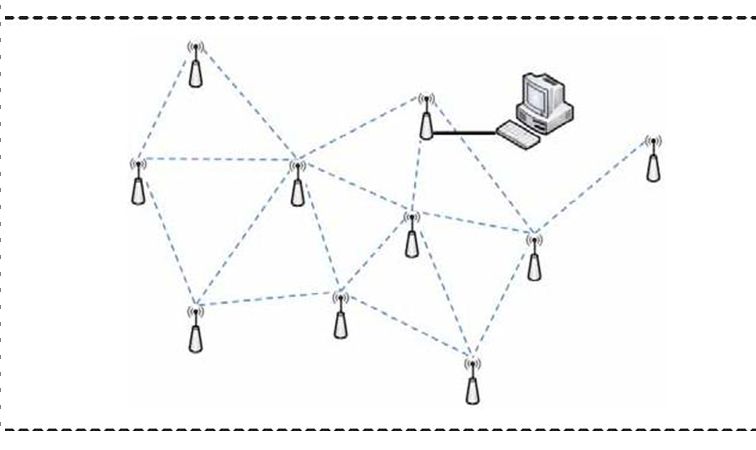
The positions of WSN nodes are random, and the nodes can be moved, sheltered and interfered with. The topology of mesh networks have great advantages in fl exibility and reliability compared with other network topologies. The self-organizing management approach of network nodes can greatly improve the robustness of the network, resulting in a smart mesh networking technology, as shown in Figure 3-9. In smart mesh ad hoc networking technology, the node fi rst monitors the neighbour nodes and measures the signal strength, and then it selects the appropriate neighbour node for time synchronization and sends a joining request. Then the neighbour node delivers the request to the gateway. The gateway receives the request and assigns network resources for the node. Based on the mesh network, the sensor network nodes can be assigned with two or more transmission paths to improve the reliability of network.
无线传感器网络节点的位置是随机的,节点可以被移动、屏蔽和干扰。与其他网络拓扑相比,Mesh网络的拓扑结构在FL灵活性和可靠性方面具有很大的优势。网络节点的自组织管理方法可以大大提高网络的健壮性,从而产生一种智能网状网络技术,如图3-9所示。在智能网Ad Hoc网络技术中,节点FI RST监视邻居节点并测量信号强度,然后选择合适的邻居节点进行时间同步,并发送连接请求。然后邻居节点将请求传递给网关。网关接收请求并为节点分配网络资源。基于网状网络,传感器网络节点可以被分配两个或多个传输路径,以提高网络的可靠性。
Low cost IP interconnection technology
低成本IP互联技术
The design of early sensor networks commonly used internal addresses to manage the sensor network nodes. The address length was relatively short and suitable for implementing in low-power embedded sensor network nodes. However, the internal address management method is not compatible with the IP method of the internet, which increased the difficulty of interacting between the sensor network nodes and the traditional IP network nodes. Therefore, there is a need to resolve the connectivity problem of WSN and IP network.
设计早期的传感器网络常用的内部地址来管理传感器网络节点。地址长度相对较短,适合在低功耗嵌入式传感器网络节点中实现。然而,内部地址管理方法与互联网的IP方法不兼容,这增加了传感器网络节点与传统IP网络节点之间交互的差异。因此,需要解决无线传感器网络和IP网络的连通性问题。
Self-adaptive flow control technology
自适应流量控制技术
One of the differences between WSNs and traditional wired networks is the instability of wire-less communication. In WSNs, the communication between nodes is susceptible to interference and occlusion, resulting in signal transmission failure. The traditional network is a stable wired network, which data will only be lost due to congestion. The principle of flow control is that the data sender adjusts the sending traffi c according to the loss situation of data transmission. When data loss occurs, the sender decreases the transmission rate. And when the data is not lost, the sender increases the transmission rate. Such flow control mechanisms are no longer suitable for WSNs [23], because the data loss in sensor networks is mostly caused by congestion, interference and occlusion. Purely decreasing the transmission rate cannot solve the problem, but only lowers the network performance.
无线传感器网络与传统有线网络的区别之一是无线通信的不稳定性。在WSNs中,节点之间的通信容易受到干扰和闭塞,导致信号传输失败。传统的网络是一个稳定的有线网络,数据只会因拥塞而丢失。流量控制的原理是数据发送方根据数据传输的丢失情况来调整发送业务。当发生数据丢失时,发送方降低传输速率。当数据不丢失时,发送器增加传输速率。这样的流量控制机制不再适合于WSNs,因为传感器网络中的数据丢失主要是由拥塞、干扰和闭塞引起的。单纯降低传输速率不能解决问题,而只能降低网络性能。
In order to solve the network performance degradation problem in unstable transmission conditions, adaptive flow control is proposed. Adaptive flow control checks the reason for packet loss and adjusts the transmission flow. Mean-while, according to the quality of the link and the number of transmission errors, the best transmission rate for the data transmission between nodes is prioritized to obtain good network stability while considering the transmission distance and throughput.
为了解决不稳定传输条件下的网络性能退化问题,提出了自适应流量控制。自适应流量控制检查分组丢失的原因,并调整传输流量。同时,根据链路质量和传输差错数,优先考虑节点间数据传输的最佳传输速率,在考虑传输距离和吞吐量的前提下,获得良好的网络稳定性。
上一篇:节气门位置传感器
